Whos Who in a Food Chain Biology Diagrams Learn what a food chain is, how it works, and the types of food chains with examples. A food chain shows the order of organisms that eat each other and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Learn how food chains work in this video from our Grade 4 science course. View our full list of course offerings:https://www.virtualelementaryschool.com/regi
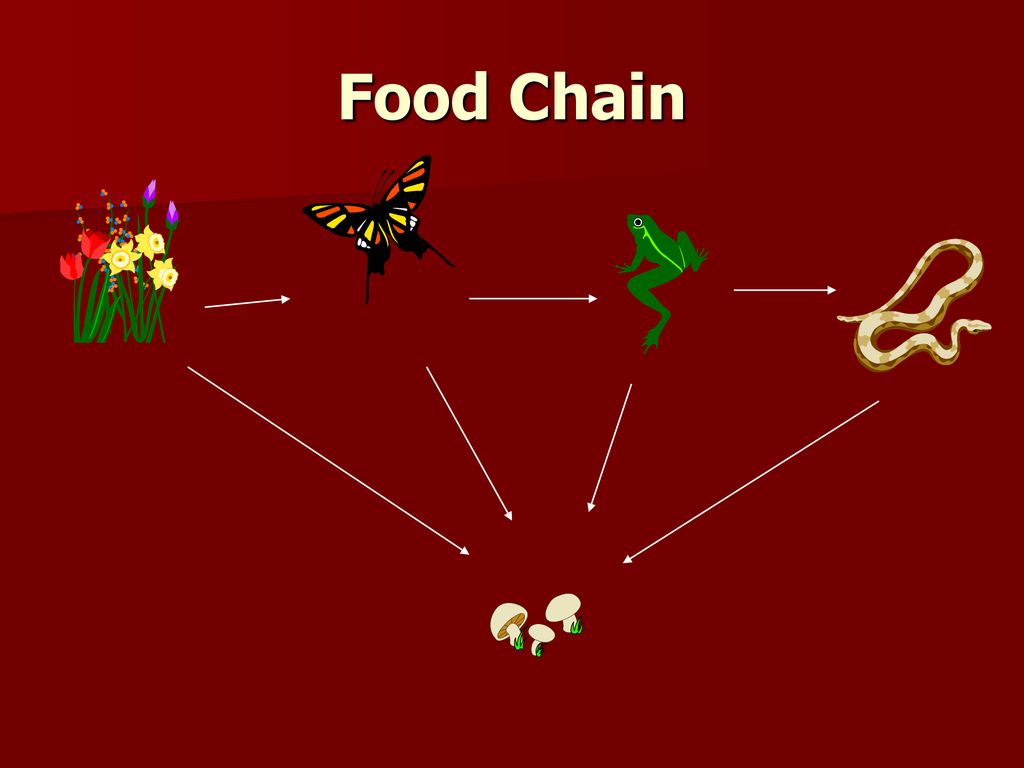
How Does a Food Chain Work? A food chain operates on energy transfer across trophic levels, where each level represents a stage in the chain. Producers at the base capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy, which moves up the chain as each consumer feeds on the one below it. Decomposers break down dead organisms, returning Autotrophs: The Producers. As mentioned earlier, a food chain starts with the primary producers at the base who can make their own food. These organisms are called autotrophs.Autotrophs can make their own food using their own organic compounds from simple molecules like carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight. Autotrophs come in two types:. 1.
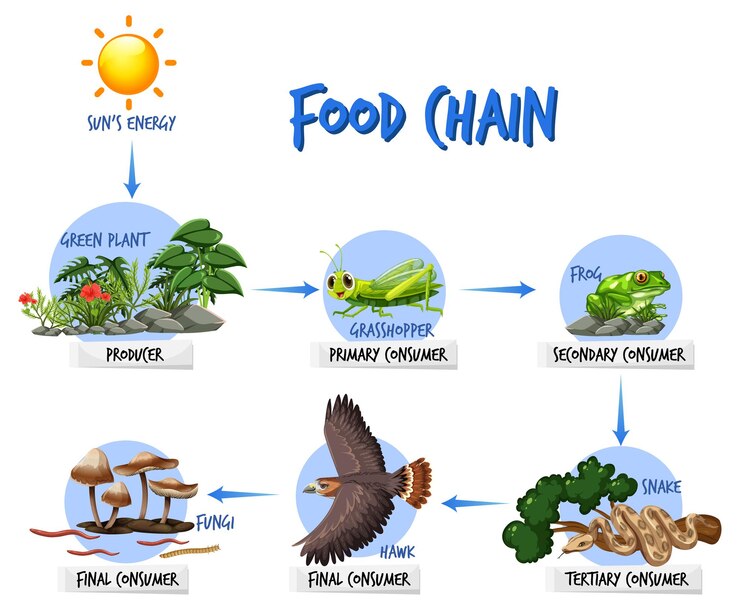
The Intricate Web of Life: How Food Chains Work Biology Diagrams
The figure 8.12 explains the flow of energy through a typical food chain. Two types of food chains are present in ecosystems. They are the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain. Grazing food chain. Grazing animals play an important role in the transfer of energy to the carnivores in this type of food chain, hence the name grazing food
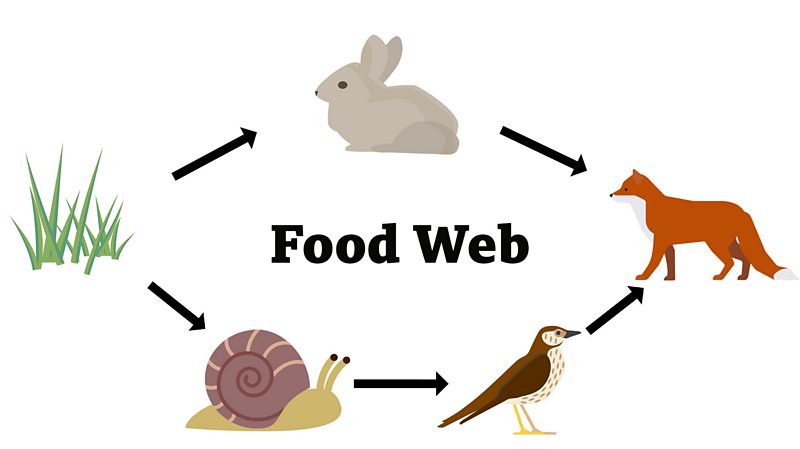
You can find interesting examples of food chains in habitats ranging from forests to lakes. For instance, meerkats can be a top predator in one food chain by eating insects and worms. However, in other food chains, predators like eagles can eat the meerkats. An example of a simple food chain starts with grass, which is a producer. A food chain represents a single, linear pathway of energy flow between organisms, whereas a food web is a more complex interconnection of multiple food chains within an ecosystem. Food webs take into account the various feeding relationships that occur between species, highlighting that most organisms consume or are consumed by multiple other

Food Chain: How Energy Flows From Autotrophs To Heterotrophs? Biology Diagrams
How Do Food Chains Work? A food chain starts with sunlight, which is absorbed by plants and used to create food through photosynthesis. Herbivores feed on plants, gaining the energy stored in them. Carnivores then eat these herbivores, gaining the energy that the plants first absorbed from the sun. Higher-level predators or scavengers may

Because energy, in the form of heat, is lost at each step, or trophic level, chains do not normally encompass more than four or five trophic levels. People can increase the total food supply by cutting out one step in the food chain: instead of consuming animals that eat cereal grains, the people themselves consume the grains. Because the food chain is made shorter, the total amount of energy
