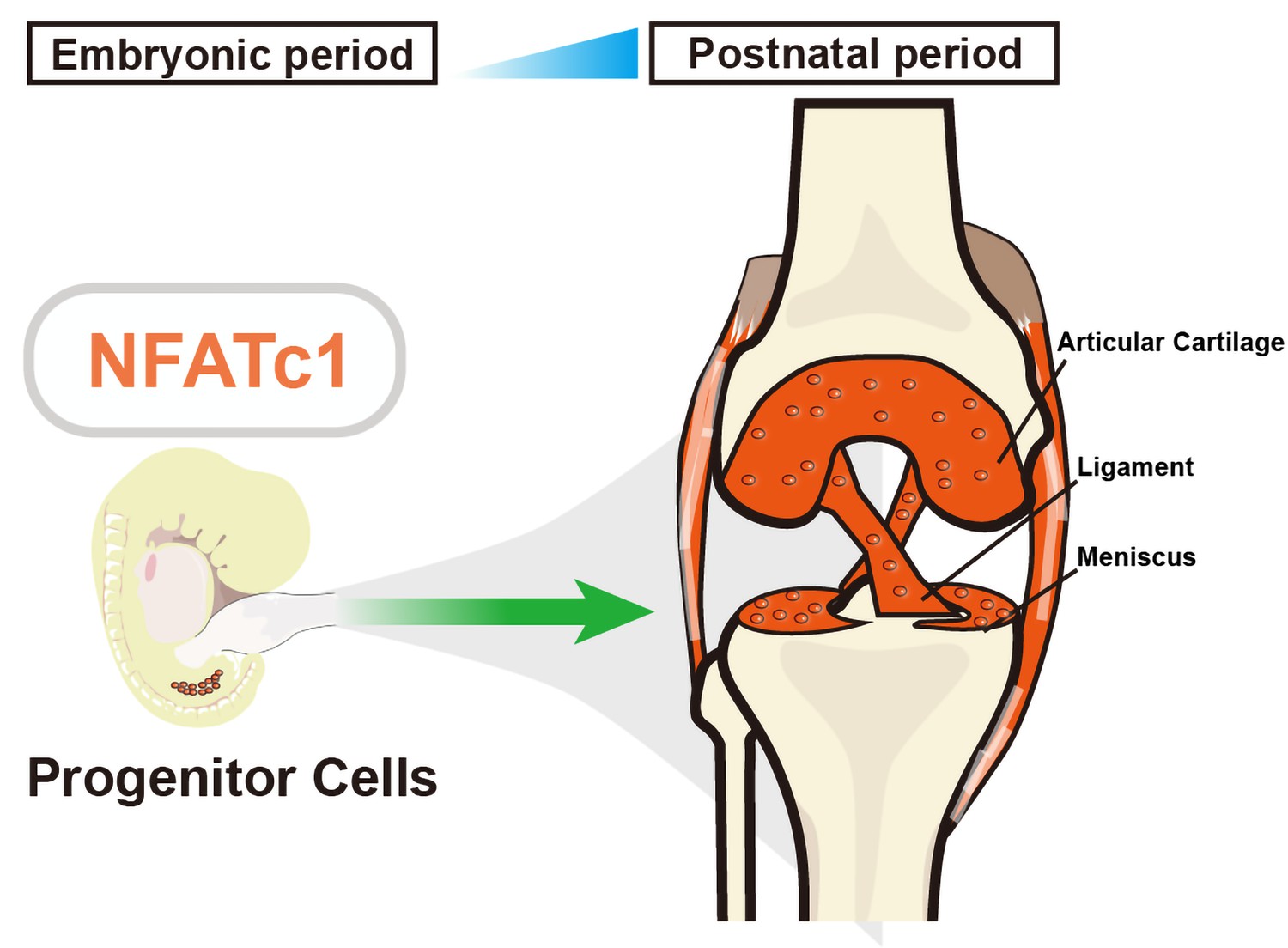
The Basic Science of Articular Cartilage Structure Composition and Biology Diagrams Articular cartilage is the highly specialized connective tissue of diarthrodial joints. Its principal function is to provide a smooth, lubricated surface for articulation and to facilitate the transmission of loads with a low frictional coefficient ().Articular cartilage is devoid of blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves and is subject to a harsh biomechanical environment. Osteoarthritis is a disease affecting the whole joint; however, the articular cartilage (a subset of hyaline cartilage) within the joint is the most affected tissue. Pei M. Meniscus, articular cartilage and nucleus pulposus: a comparative review of cartilage-like tissues in anatomy, development and function. Cell Tissue Res. 2017 Oct; 370 The articular cartilage is a type of specialized connective tissue present in synovial joints. It is composed of hyaline cartilage with a dense extracellular matrix and scattered specialized cells of the cartilage known as chondrocytes.. The extracellular matrix is mainly composed of collagen, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins which help to retain the water molecules in the matrix.

Since articular cartilage lacks its own blood supply, it relies on the diffusion of nutrients and oxygen from the synovial fluid to sustain cellular functions. This nutrient exchange is facilitated by regular joint movement, which promotes fluid circulation and ensures the delivery of essential molecules to the cartilage.
Anatomy, Cartilage Biology Diagrams
Following an intra-articular fracture, in addition to mechanical disruption and cartilage necrosis, the following inflammatory cytokines are released, contributing to articular damage and the eventual development of post-traumatic arthritis:IL-1β, TNF-α, nitric oxide, matrix metalloproteinases, aggrecans, and damage associated molecular patterns.
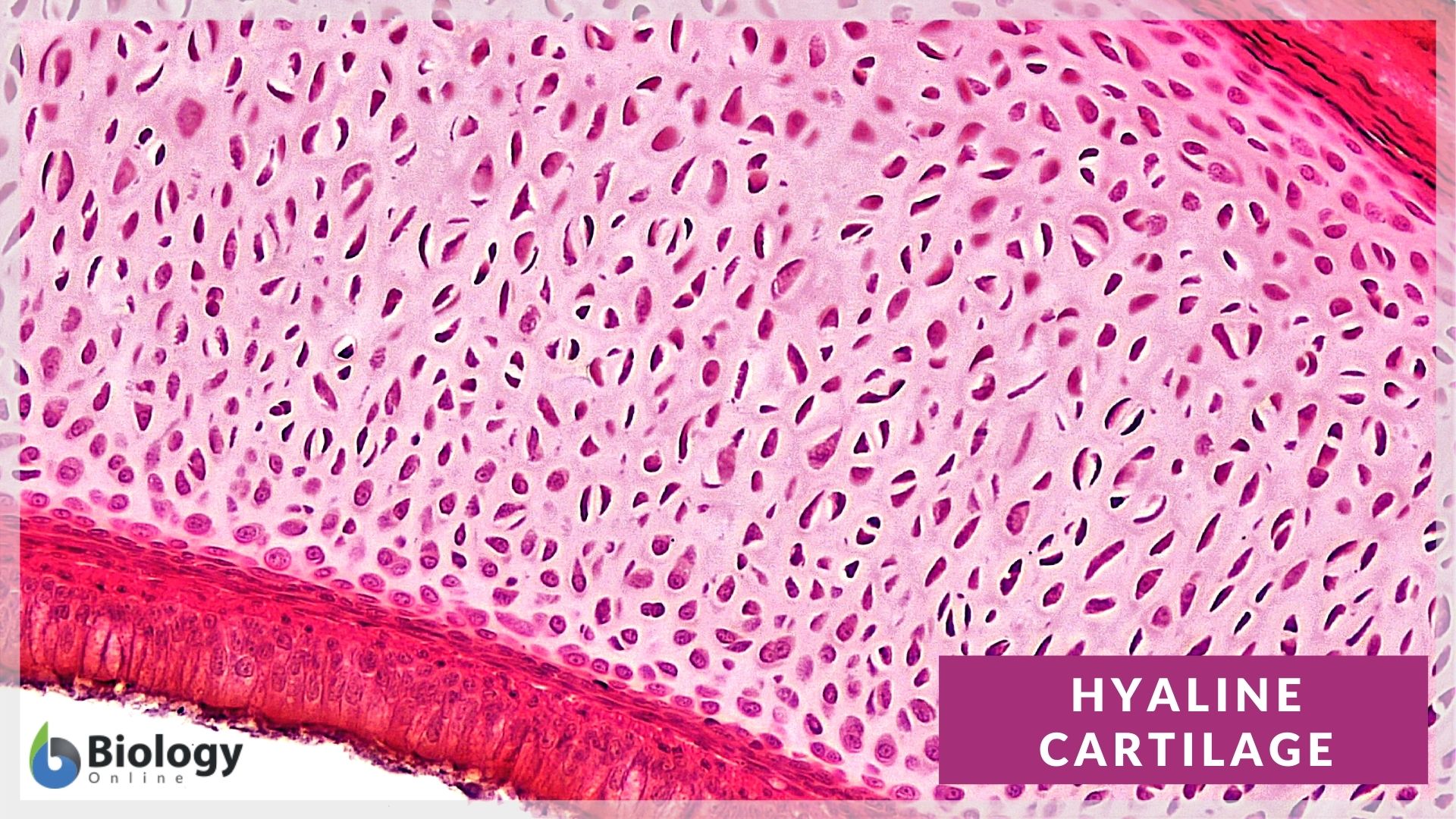
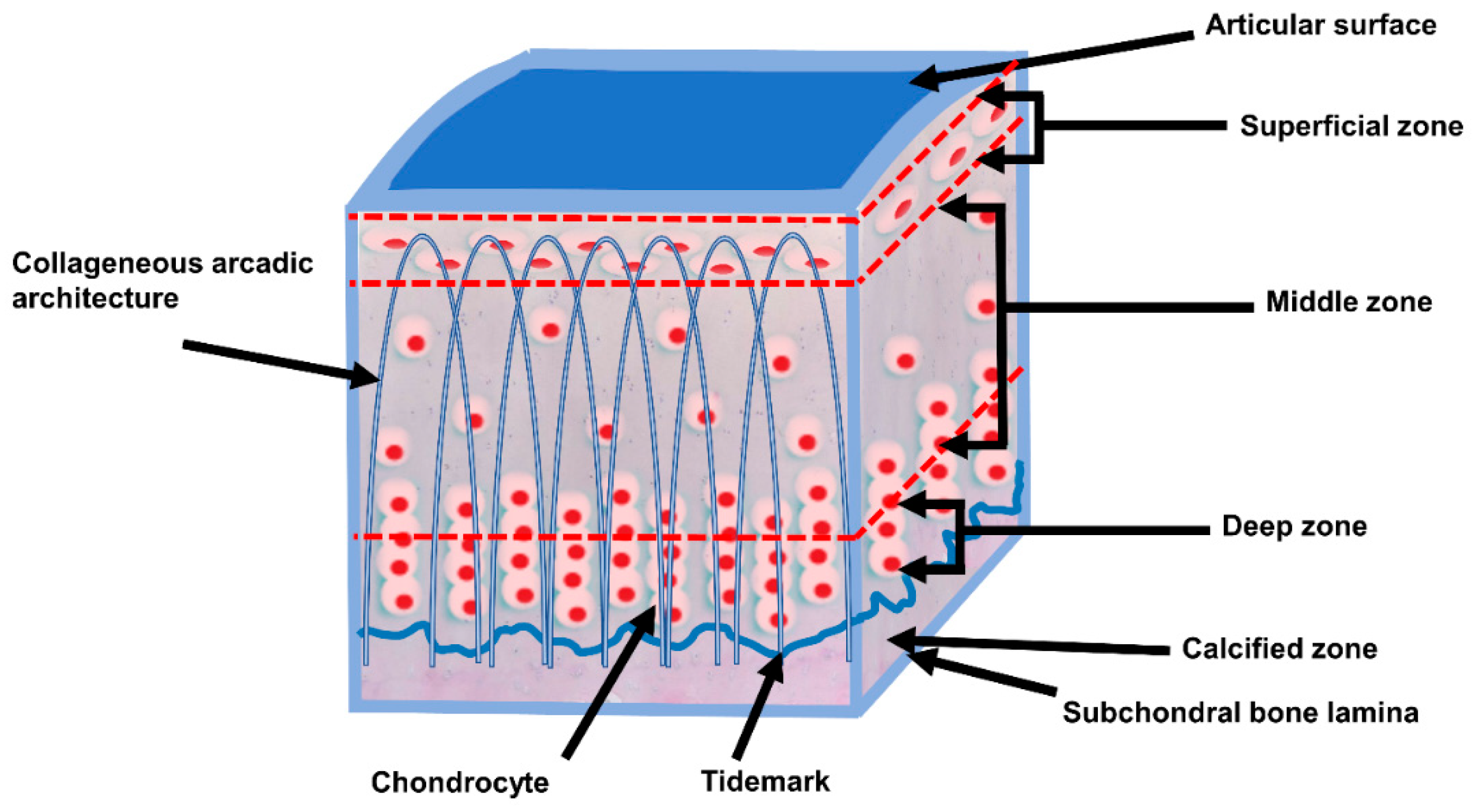
Articular cartilage (histological slide) Additionally, a glycoprotein known as lubricin that is abundant in the superficial layer of cartilage and synovial fluid plays a major role in bio-lubrication and wear protection of cartilage.. Layers. The layers of articular cartilage are defined by zones. Starting from the subchondral bone, there is a tidemark that is deep to the basal layer and
Definition and Function Biology Diagrams
Articular (hyaline) cartilage anatomy. Hyaline articular cartilage is an aneural, avascular, and alymphatic structure. Chondrocytes form only 1-5% of the volume of articular cartilage. Chondrocytes receive their nutrition by diffusion through the matrix. A further function of articular cartilage is the ability for that part of the anatomy to move on one or more planes. The joint range of movement depends on the specific type of diarthroidal joint. Where Is Articular Cartilage Found. Articular cartilage locations are found throughout the body. Maintaining healthy articular cartilage through proper nutrition, exercise, and avoiding excessive stress on the joints is key to preserving joint health in the long term. Prioritizing care for this vital tissue can significantly impact overall mobility and quality of life. Common Issues and Diseases Affecting Articular Cartilage
