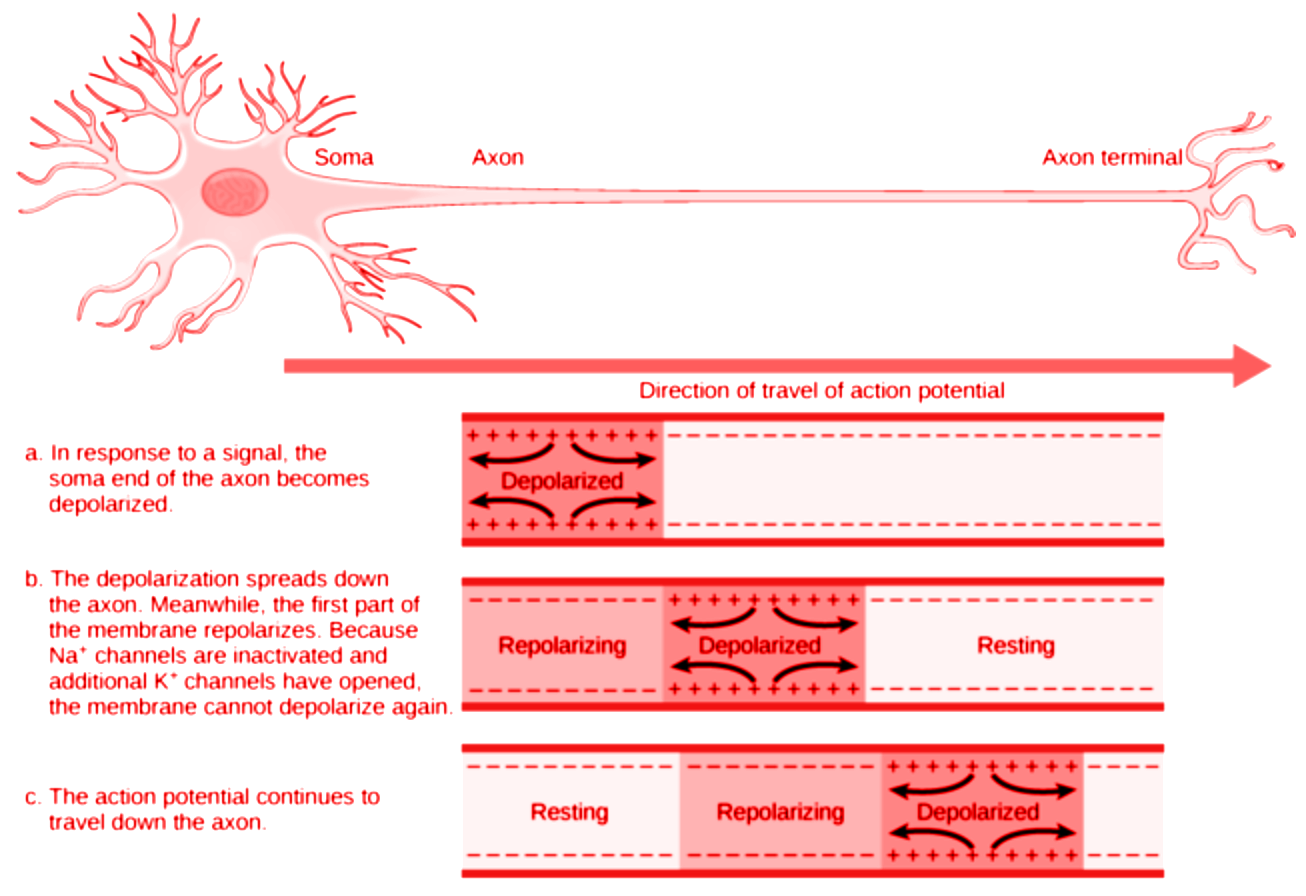
5 SEM III PAPER 1 TRANSMISSION OF NERVE IMPULSE THROUGH SYNAPSE Biology Diagrams In medullated nerve fibres (white fibres), the impulse jumps from node to node, it is called saltatory propagation (Fig. 1.21). It increases the speed of nerve impulse which is about 20 times faster in medulated than in non-medullated nerve fibres. The speed of transmission of nerve impulse also depends upon the diameter of the fibre.

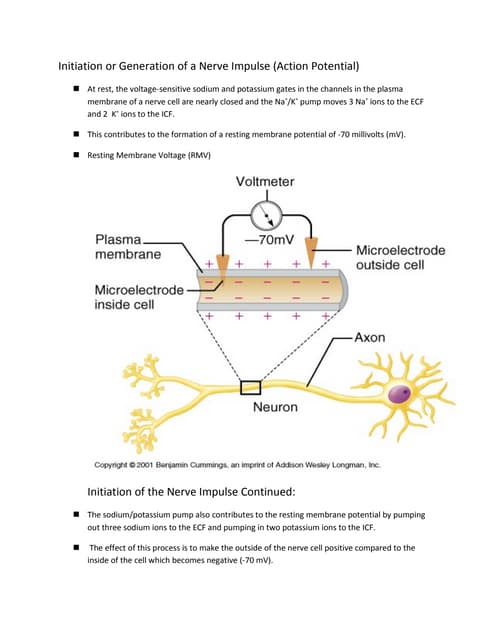
This page titled 35.5: How Neurons Communicate - Nerve Impulse Transmission within a Neuron- Action Potential is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless. Action Potential. An action potential, also called a nerve impulse, is an electrical charge that travels along the membrane of a neuron.It can be generated when a neuron's membrane potential is changed by chemical signals from a nearby cell. In an action potential, the cell membrane potential changes quickly from negative to positive as sodium ions flow into the cell through ion channels
Nervous system - Signaling, Neurons, Impulses Biology Diagrams
Figure 1.Events that characterize the transmission of a nerve impulse. The following four steps describe the initiation of an impulse to the "resetting" of a neuron to prepare for a second stimulation: Action potential. Unlike a graded potential, an action potential is capable of traveling long distances.

Nerve Impulse Transmission within a Neuron. For the nervous system to function, neurons must be able to send and receive signals. These signals are possible because each neuron has a charged cellular membrane (a voltage difference between the inside and the outside), and the charge of this membrane can change in response to neurotransmitter molecules released from other neurons and
Transmission of Nerve Impulses Biology Diagrams
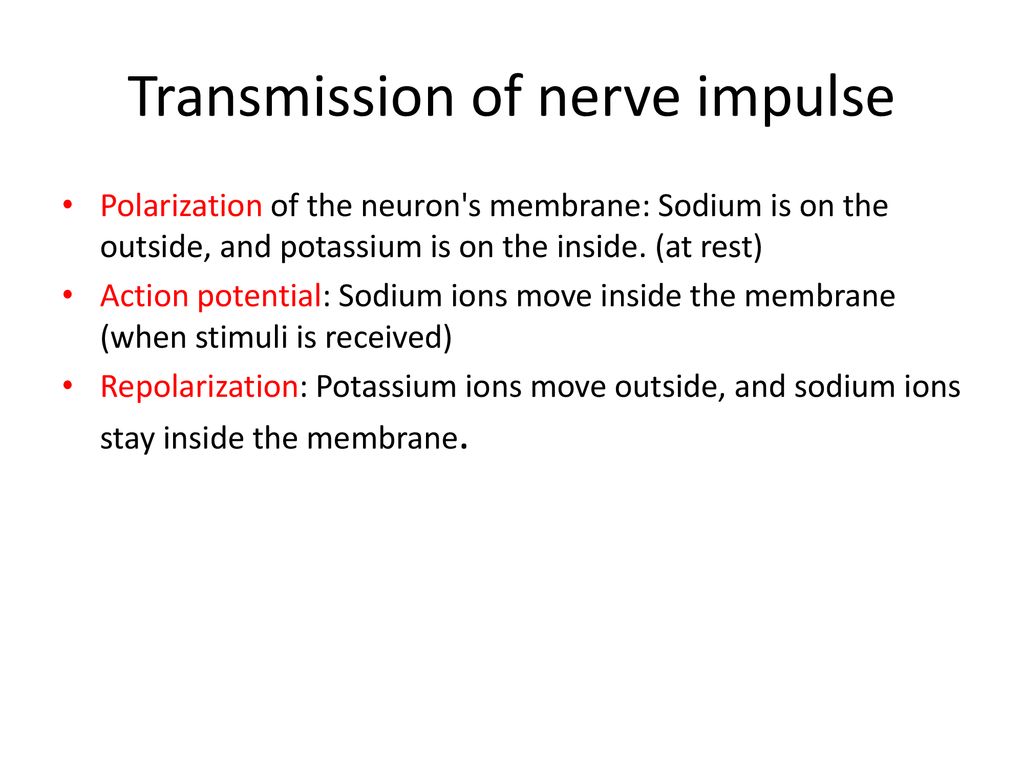
Anatomy and Physiology Nervous System www.physiotherapyphd.com Conduction of Nerve Impulse Nerve Impulse transmission: Transmission of nerve impulse along nerve fibre can be summarized in three steps 1. Polarization (Resting Potential) 2. Depolarization (Action Potential) 3. Repolarization Neurobiology is a vast and rapidly expanding field with significant clinical and technological implications. Far-reaching questions, such as what composes human personalities and the development of consciousness, are boiled down to quantitative processes. At the root of this field is the neuron and how information gets transferred throughout the body via electrochemical signals. This article
Synapse Chemical transmission of a nerve impulse at the synapse. The arrival of the nerve impulse at the presynaptic terminal stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap. The binding of neurotransmitters to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane stimulates the regeneration of the action potential in the postsynaptic neuron
